synthesizer.emission_models.transformers.dust_attenuation¶
A module containing dust attenuation functionality.
This module contains classes for dust attenuation laws. These classes provide a way to calculate the optical depth and transmission curves for a given dust model.
Example usage:
# Create a power law dust model with a slope of -1.0
dust_model = PowerLaw(slope=-1.0)
# Calculate the transmission curve
transmission = dust_model.get_transmission(
0.33, np.linspace(1000, 10000, 1000)
)
Functions
- synthesizer.emission_models.transformers.dust_attenuation.Li08(lam, UV_slope, OPT_NIR_slope, FUV_slope, bump, model)[source]¶
Drude-like parametric expression for the attenuation curve from Li+08.
- Parameters:
lam (np.ndarray of float) – The wavelengths (AA units) at which to calculate transmission.
UV_slope (float) – Dimensionless parameter describing the UV-FUV slope
OPT_NIR_slope (float) – Dimensionless parameter describing the optical/NIR slope
FUV_slope (float) – Dimensionless parameter describing the FUV slope
bump (float) – Dimensionless parameter describing the UV bump strength (0< bump <1)
model (str) – Via this parameter one can choose one of the templates for extinction/attenuation curves from: Calzetti, SMC, MW (R_V=3.1), and LMC
- Returns:
tau/tau_v at each input wavelength (lam)
- Return type:
np.ndarray of float/float
- synthesizer.emission_models.transformers.dust_attenuation.N09Tau(lam, slope, cent_lam, ampl, gamma)[source]¶
Generate the transmission curve for the Noll+2009 attenuation curve.
Attenuation curve using a modified version of the Calzetti attenuation (Calzetti+2000) law allowing for a varying UV slope and the presence of a UV bump; from Noll+2009
References
https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2009A%26A…499…69N
- Parameters:
lam (np.ndarray of float) – The input wavelength array (expected in AA units, global unit).
slope (float) – The slope of the attenuation curve.
cent_lam (float) – The central wavelength of the UV bump, expected in AA.
ampl (float) – The amplitude of the UV-bump.
gamma (float) – The width (FWHM) of the UV bump, in AA.
- Returns:
- V-band normalised optical depth for
given wavelength
- Return type:
np.ndarray of float
Classes
- class synthesizer.emission_models.transformers.dust_attenuation.AttenuationLaw(description, required_params=('tau_v',), require_tau_v=True)[source]¶
The base class for all attenuation laws.
A child of this class should define it’s own get_tau method with any model specific behaviours. This will be used by get_transmission (which itself can be overloaded by the child if needed).
- description¶
A description of the type of model. Defined on children classes.
- Type:
str
- required_params¶
The name of any required parameters needed by the transformer when transforming an emission. These should either be available from an emitter or from the EmissionModel itself. If they are missing an exception will be raised.
- Type:
tuple
- get_transmission(tau_v, lam, **dust_curve_kwargs)[source]¶
Compute the transmission curve.
Returns the transmitted flux/luminosity fraction based on an optical depth at a range of wavelengths.
- Parameters:
tau_v (float/np.ndarray of float) – Optical depth in the V-band. Can either be a single float or array.
lam (np.ndarray of float) – The wavelengths (with units) at which to calculate transmission.
**dust_curve_kwargs (dict) – Additional keyword arguments to be passed to the dust curve which have been defined on the emitter or model.
- Returns:
The transmission at each wavelength. Either (lam.size,) in shape for singular tau_v values or (tau_v.size, lam.size) tau_v is an array.
- Return type:
np.ndarray of float
- plot_attenuation(lam, fig=None, ax=None, label=None, figsize=(8, 6), show=True, **kwargs)[source]¶
Plot the attenuation curve.
- Parameters:
lam (np.ndarray of float) – The wavelengths (with units) at which to calculate transmission.
fig (matplotlib.figure.Figure) – The figure to plot on. If None, a new figure will be created.
ax (matplotlib.axes.Axes) – The axis to plot on. If None, a new axis will be created.
label (str) – The label to use for the plot.
figsize (tuple) – The size of the figure to create if fig is None.
show (bool) – Whether to show the plot.
**kwargs (dict) – Keyword arguments to be provided to the plot call.
- Returns:
The figure and axis objects.
- Return type:
fig, ax
- plot_transmission(tau_v, lam, fig=None, ax=None, label=None, figsize=(8, 6), show=True)[source]¶
Plot the transmission curve.
- Parameters:
tau_v (float/np.ndarray of float) – Optical depth in the V-band. Can either be a single float or array.
lam (np.ndarray of float) – The wavelengths (with units) at which to calculate transmission.
fig (matplotlib.figure.Figure) – The figure to plot on. If None, a new figure will be created.
ax (matplotlib.axes.Axes) – The axis to plot on. If None, a new axis will be created.
label (str) – The label to use for the plot.
figsize (tuple) – The size of the figure to create if fig is None.
show (bool) – Whether to show the plot.
- Returns:
The figure and axis objects.
- Return type:
fig, ax
Examples using synthesizer.emission_models.transformers.dust_attenuation.AttenuationLaw¶
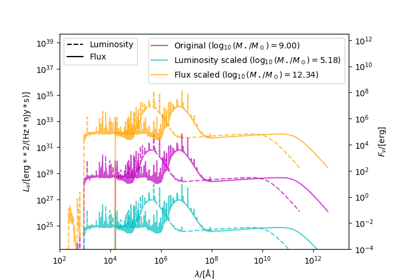
An example showing how to scale a galaxy’s mass by luminosity/flux.
- class synthesizer.emission_models.transformers.dust_attenuation.Calzetti2000(slope=0, cent_lam=unyt_quantity(2175, 'Å'), ampl=0, gamma=unyt_quantity(350, 'Å'))[source]¶
Calzetti attenuation curve.
This includes options for the slope and UV-bump implemented in Noll et al. 2009.
- slope¶
The slope of the attenuation curve.
- Type:
float
- cent_lam¶
The central wavelength of the UV bump, expected in AA.
- Type:
float
- ampl¶
The amplitude of the UV-bump.
- Type:
float
- gamma¶
The width (FWHM) of the UV bump, in AA.
- Type:
float
- get_tau(lam)[source]¶
Calculate V-band normalised optical depth.
(Uses the N09Tau function defined above.)
- Parameters:
lam (float/np.ndarray of float) – An array of wavelengths or a single wavlength at which to calculate optical depths (in AA, global unit).
- Returns:
The V-band noramlised optical depth.
- Return type:
float/array-like, float
- get_tau_at_lam(lam)[source]¶
Calculate optical depth at a wavelength.
(Uses the N09Tau function defined above.)
- Parameters:
lam (float/array-like, float) – An array of wavelengths or a single wavlength at which to calculate optical depths (in AA, global unit).
- Returns:
- float/array-like, float
The optical depth.
- class synthesizer.emission_models.transformers.dust_attenuation.DraineLiGrainCurves(grid_name, grid_dir, grain_dict=None)[source]¶
Draine and Li extinction curves.
Draine and Li extinction curves obtained from pre-processing the extinction efficiencies for the required grain size distribution. This is done in grid-generation repo under ‘grid-generation/src/synthesizer_grids/dust/ create_dustextcurve_draine_li.py’ for the required dust parameters. Currently only implemented for 2 grain sizes of graphites and silicates, and 1 size of PAHs.
- grid_name¶
Name of the extinction curve grid (without hdf5 extension)
- Type:
string
- grid_dir¶
Location of the grid
- Type:
string
- grain_dict¶
Dictionary containing the grain type (‘graphite’ or ‘silicate’ or ‘pahionised’ or ‘pahneutral’) and their corresponding centre of the grain size distribution in microns. E.g. grain_dict = {‘graphite’: [0.01, 0.1]}
- Type:
Dict
- get_tau(lam, sigmalos_H=None, **sigmalos_dust)[source]¶
Calculate optical depth normalised at V-band at a wavelength.
- Parameters:
lam (float/array-like, float) – An array of wavelengths or a single wavlength at which to calculate optical depths (in AA, global unit).
sigmalos_H (unyt array) – Line-of-sight H density in units of Msun/pc^2
(Dict (sigmalos_dust) – unyt_array): Dictionary containing the different line-of-sight dust density of the dust components. This should follow the format ‘sigmalos_{grain_type}_a{grain_bin_centre}um’: unyt_array (units of Msun/pc^2). The function will unpack the contents.
- Returns:
- optical depth/optical depth at V-band (unyt_array, float)
The optical depth at the given wavlength ((N_dtg, N_lambda) if sigmalos input is array-like, otherwise shape (N_lambda,)). Dimensionless
- get_tau_at_lam(lam, sigmalos_H=None, **sigmalos_dust)[source]¶
Calculate optical depth at a wavelength.
- Parameters:
lam (unyt_array, float) – An array of wavelengths or a single wavlength at which to calculate optical depths (in AA, global unit).
sigmalos_H (unyt array) – Line-of-sight H density in units of Msun/pc^2
(Dict (sigmalos_dust) – unyt_array): Dictionary containing the different line-of-sight dust density of the dust components. This should follow the format ‘sigmalos_{grain_type}_a{grain_bin_centre}um’: unyt_array (units of Msun/pc^2). The function will unpack the contents.
- Returns:
- optical depth (unyt_array, float)
The optical depth at the given wavlength ((N_dtg, N_lambda) if sigmalos input is array-like, otherwise shape (N_lambda,)). Dimensionless
- get_transmission(tau_v=None, lam=None, **dust_curve_kwargs)[source]¶
Compute the transmission curve.
Returns the transmitted flux/luminosity fraction based on an optical
depth at a range of wavelengths.
- Parameters:
tau_v (None) – Optical depth at V-band, not required here.
lam (np.ndarray of float) – The wavelengths (with units) at which to calculate transmission.
**dust_curve_kwargs (dict) – Additional keyword arguments to be passed to the dust curve which have been defined on the emitter or model.
- Returns:
The transmission at each wavelength
- Return type:
np.ndarray of float
- class synthesizer.emission_models.transformers.dust_attenuation.GrainModels(model='WD01', submodel='SMCBar')[source]¶
Grain model dust attenuation curves.
These models are based on dust grain size, composition, and shape distributions constrained by observations of extinction, abundances, emission, and polarization. Some of these models can be used to estimate extinction at wavelengths inaccessible to observations (e.g., extreme UV below 912 Å). These models are taken from the astropy affiliated dust-extinction package (https://dust-extinction.readthedocs.io/en/latest/ for details). By default, we will use the Weingarter & Draine 2001 (WD01) models, and the submodel for the SMC bar.)
- model¶
The dust grain model used. Available models are:
DBP90: Desert, Boulanger, & Puget 1990, A&A, 237, 215 WD01: Weingartner & Draine 2001, ApJ, 548, 296 D03: Draine 2003, ARA&A, 41, 241; Draine 2003, ApJ, 598, 1017 ZDA04: Zubko, Dwek, & Arendt 2004, ApJS, 152, 211 C11: Compiegne et al. 2011, A&A, 525, 103 J13: Jones et al. 2013, A&A, 558, 62 HD23: Hensley & Draine 2023, ApJ, 948, 55 Y24: Ysard et al. 2024, A&A, 684, 34
- Type:
str
- submodel¶
The submodel to use within the main grain model. The submodels available for the different models listed below. All of them are self-explanatory with the RV defining the normalisation of the extinction curve, where RV = AV / E(B-V). DBP90: MWRV31 WD01 MWRV31, MWRV40, MWRV55, LMCAvg, LMC2, SMCBar D03: MWRV31, MWRV40, MWRV55 ZDA04: MWRV31 C11: MWRV31 J13: MWRV31 HD23: MWRV31 Y24: MWRV31
- Type:
str
- get_tau(lam, interp='slinear')[source]¶
Calculate V-band normalised optical depth.
- Parameters:
lam (float/np.ndarray of float) – An array of wavelengths or a single wavlength at which to calculate optical depths (in AA, global unit).
interp (str) – The type of interpolation to use. Can be ‘linear’, ‘nearest’, ‘nearest-up’, ‘zero’, ‘slinear’, ‘quadratic’, ‘cubic’, ‘previous’, or ‘next’. ‘zero’, ‘slinear’, ‘quadratic’ and ‘cubic’ refer to a spline interpolation of zeroth, first, second or third order. Uses scipy.interpolate.interp1d.
- Returns:
The optical depth.
- Return type:
float/np.ndarray of float
- get_tau_at_lam(lam, interp='slinear')[source]¶
Calculate optical depth at a wavelength.
- Parameters:
lam (float/array-like, float) – An array of wavelengths or a single wavlength at which to calculate optical depths (in AA, global unit).
interp (str) – The type of interpolation to use. Can be ‘linear’, ‘nearest’, ‘nearest-up’, ‘zero’, ‘slinear’, ‘quadratic’, ‘cubic’, ‘previous’, or ‘next’. ‘zero’, ‘slinear’, ‘quadratic’ and ‘cubic’ refer to a spline interpolation of zeroth, first, second or third order. Uses scipy.interpolate.interp1d.
- Returns:
- float/array-like, float
The optical depth.
- class synthesizer.emission_models.transformers.dust_attenuation.MWN18[source]¶
Milky Way attenuation curve used in Narayanan+2018.
- data¶
The data describing the dust curve, loaded from MW_N18.npz.
- Type:
np.ndarray of float
- tau_lam_v¶
The V band optical depth.
- Type:
float
- get_tau(lam, interp='cubic')[source]¶
Calculate V-band normalised optical depth.
- Parameters:
lam (float/array, float) – An array of wavelengths or a single wavlength at which to calculate optical depths (in AA, global unit).
interp (str) – The type of interpolation to use. Can be ‘linear’, ‘nearest’, ‘nearest-up’, ‘zero’, ‘slinear’, ‘quadratic’, ‘cubic’, ‘previous’, or ‘next’. ‘zero’, ‘slinear’, ‘quadratic’ and ‘cubic’ refer to a spline interpolation of zeroth, first, second or third order. Uses scipy.interpolate.interp1d.
- Returns:
The optical depth.
- Return type:
float/array, float
- get_tau_at_lam(lam, interp='cubic')[source]¶
Calculate the optical depth at a wavelength.
- Parameters:
lam (float/array, float) – An array of wavelengths or a single wavlength at which to calculate optical depths (in AA, global unit).
interp (str) – The type of interpolation to use. Can be ‘linear’, ‘nearest’, ‘nearest-up’, ‘zero’, ‘slinear’, ‘quadratic’, ‘cubic’, ‘previous’, or ‘next’. ‘zero’, ‘slinear’, ‘quadratic’ and ‘cubic’ refer to a spline interpolation of zeroth, first, second or third order. Uses scipy.interpolate.interp1d.
- Returns:
- float/array, float
The optical depth.
- class synthesizer.emission_models.transformers.dust_attenuation.ParametricLi08(UV_slope=44.9, OPT_NIR_slope=7.56, FUV_slope=61.2, bump=0.0, model='Calzetti')[source]¶
Parametric, empirical attenuation curve.
Implemented in Li+08, Evolution of the parameters up to high-z (z=12) studied in: Markov+23a,b
- UV_slope¶
Dimensionless parameter describing the UV-FUV slope (0, 50)
- Type:
float
- OPT_NIR_slope¶
Dimensionless parameter describing the optical/NIR slope (0, 10)
- Type:
float
- FUV_slope¶
Dimensionless parameter describing the FUV slope (-1, 75)
- Type:
float
- bump¶
Dimensionless parameter describing the UV bump strength (-0.005< bump <0.06)
- Type:
float
- model¶
Fixing attenuation/extinction curve to one of the known templates: MW, SMC, LMC, Calzetti
- Type:
str
- get_tau(lam)[source]¶
Calculate V-band normalised optical depth.
(Uses the Li_08 function defined above.)
- Parameters:
lam (float/np.ndarray of float) – An array of wavelengths or a single wavlength at which to calculate optical depths (in AA, global unit).
- Returns:
The V-band normalised optical depth.
- Return type:
float/array-like, float
- get_tau_at_lam(lam)[source]¶
Calculate optical depth at a wavelength.
(Uses the Li_08 function defined above.)
- Parameters:
lam (float/array-like, float) – An array of wavelengths or a single wavlength at which to calculate optical depths (in AA, global unit).
- Returns:
- float/array-like, float
The optical depth.
- class synthesizer.emission_models.transformers.dust_attenuation.PowerLaw(slope=-1.0)[source]¶
Custom power law dust curve.
- slope¶
The slope of the power law.
- Type:
float